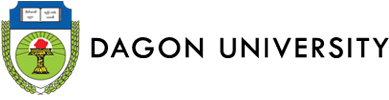Dr. Kyi Nwe Nwe Aung ဒေါက်တာကြည်နွယ်နွယ်အောင်
Position : Professor
Degree : B.Sc. (Hons:), MSc., Post graduate Diploma (Engineering Geology), Ph.D (Yangon University)
Teacher list
| Sr.No |
Department |
Name |
Position |
Education |
Thesis Title |
Field Of Specialization |
Current Research Project |
Email/Gmail |
| 1 |
Geology |
Dr. Aung May Than |
Professor (Head) |
Ph.D |
Carbonate Sedimentology of the Miocene Limestone in the Pyawbwe and Kyaukkok Formation (Lower Miocene), Kyangin Area |
Sedimentology |
1.Geochemical and Petrographical Analysis of Limestones from Hpa-an Area, Kayin State
2.Geotourism Potential Analysis on Geoheritage Sites in Hpa-an Area, Kayin State |
[email protected] |
| 2 |
Geology |
Dr. Kyi Nwe Nwe Aung |
Professor |
Ph.D |
Structural And Petrofabric Studies of The Yinmabin Area and Its environs |
Structural Geology |
|
[email protected] |
| 3 |
Geology |
Daw Than Thet Mar |
Associate Professor |
M.Sc |
Petrology Of The Hnangyi-Taungpulu Area Patheingyi Township |
Petrology |
|
[email protected] |
| 4 |
Geology |
U Zaw |
Lecturer |
M.Sc |
Petrology of Rocks of Shwethalyaung Range and Surrounding Areas, Kyaukse Township, Mandalay Region |
Petrology |
|
|
| 5 |
Geology |
Dr. Aung Myo Zaw |
Lecturer |
Ph.D |
Liquefaction Hazard Analysis And Zonation For Southern Yangon By Geotechnical And Geophysical Methods |
Enginnering Geology |
Liquefaction Potential Analysis For Central Business District (CBD) Of Yangon City By Using Nakamura Methodology |
[email protected] |
| 6 |
Geology |
U Min Han Nyein |
Assistant Lecturer |
M.Sc |
Groundwater Analysis of the Mayangone Area |
Hydrogeology |
Irrigation water analysis of the Thaegone Township, Bago Region |
[email protected] |
| 7 |
Geology |
U Ye Zaw |
Demonstrator |
M.Sc |
Granite-Related Tungsten-Tin Mineralization in Putletto area, Dawei Township, Tanintharyi Region |
Economic & Mining Geology |
Discovery of Lower Triassic (Induan- Olenekian) boundary beds from the western part of southern Shan State, Myanmar |
[email protected] |
| 8 |
Geology |
Daw Zin Nwe Khaing |
Demonstrator |
M.Res |
Assessment of Groundwater Quality of Pyin Oo Lwin area, Mandalay Region |
Hydrogeology |
The first systematic Description of Nowakia acuria (Dacryoconarida Tentaculida) from Lower Devonian Zebingyi Formation, Myanmar |
[email protected] |
| 9 |
Geology |
U Min Thu Kha |
Demonstrator |
M.Sc |
Foraminifera Distribution and Paleoecology of Okhmintaung Formation in Padaung Area, Magwe Region |
Paleontology |
|
[email protected] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Programmes Offered
- B.Sc. / B.Sc. (Hons) in Geology
- M.Sc. and M.Res. in Geology
Curriculum
B.Sc. in Geology
Fieldwork is a vital part of an Earth scientist’s training. Our field courses are designed to provide a wide range of practical exercises and field experience in geology: observing, measuring, recording, mapping, and problem-solving. A geology specialized student must take field training course from second year through final year. In final year, students must submit Geological field report and mapping projects. Term papers and project papers submission are essential that reflects their undergraduate career. The combination of lectures, practical classes, field teachings, and tutorials provide an unrivalled education in the Earth Sciences.
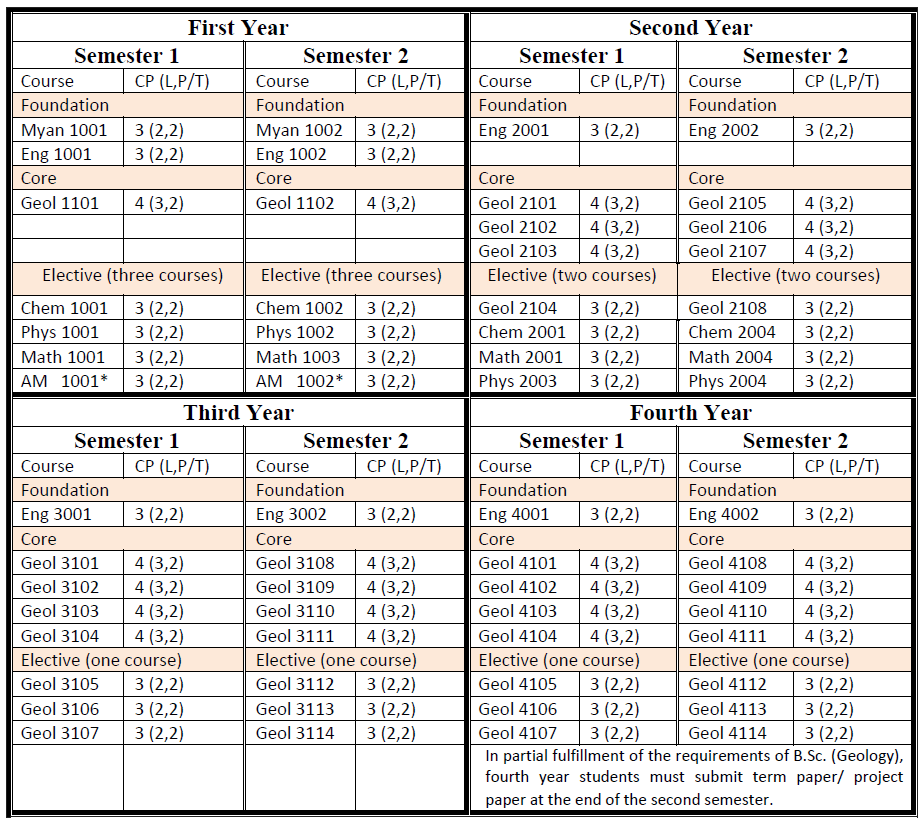
B.Sc. (Honours) in Geology
Students who passed second year with GPA ≥4 are eligible to attend B.Sc. (Hons) classes for three more years. After finished successfully, they are earned B.Sc. (Hons) degree majoring in Geology.
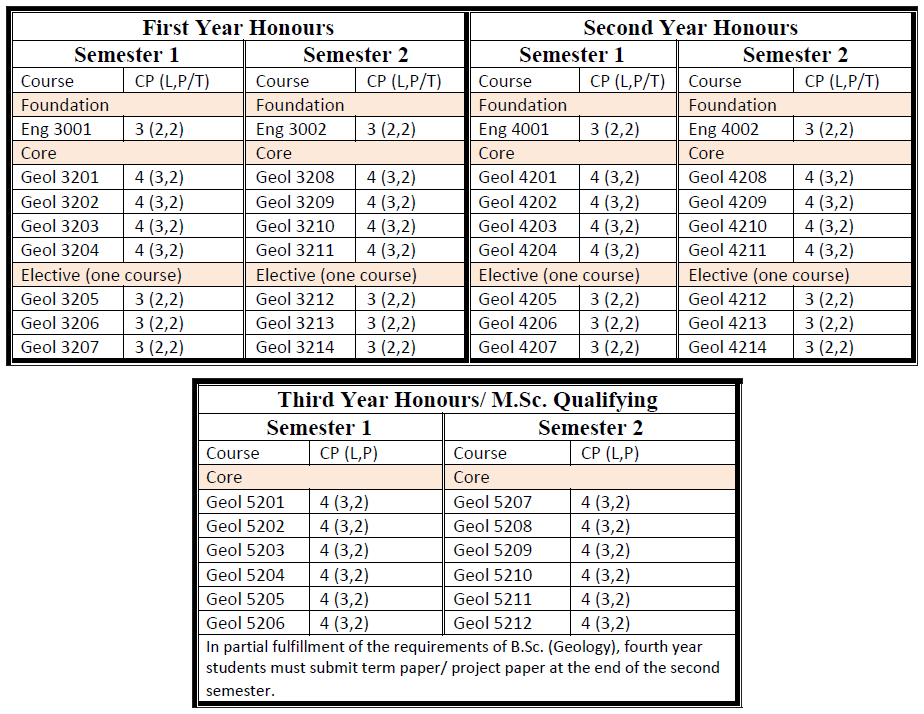
M.Sc. in Geology
Students who passed B.Sc. (Hons) with GPA ≥ 4 are eligible to attend M.Sc. classes for two more years. After finished successfully, they are earned M.Sc. degree majoring in Geology. Two specializations namely regional geology and petrology are currently offered at the department.
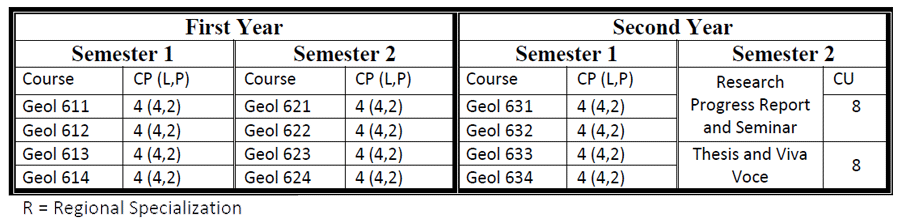
M.Res. in Geology
Students who earned CGPA ≥ 4.5 in master programs enable to leverage their research competency by attending one more year for conducting research, publishing their findings in research paper, and submission dissertation. Then, they earned the degree of Master of Research in Geology.
Students can choose the research areas and supervisors relevant to their interest. Information about the areas of research pursued at the department; and the supervisors with their research interests and expertise are announced at the department. Our well experienced faculties give close supervision, guidance and suggestion to the students. Assessment of research is made by 1) Examination board of Yangon University through the presentations of candidates and 2) Examination board of Dagon University through submission of thesis and viva voce.
Course Descriptions
This course provides to understand the basic concepts and principles of geology. It includes the following sub-heading; Planet Earth, Crystals and Minerals, Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary rocks, Metamorphic rocks, and Rock cycles.
This course aimed to students to investigate external geological processes, internal geological processes, plate tectonics, common geological structures, earth history, and earth resources.
This course deals with crystallography which includes cubic system, tetragonal system, hexagonal system, orthorhombic system, monoclinic system, triclinic system, twining, crystal chemistry, and crystal structure.
Structural geology concerns with the architecture of rocks that has result from deformation; and form, arrangement and internal structure of the rocks. Wider aspect of continental and oceanic of global structure referred to as tectonics. This course includes structural deformation, fractures, folding, faulting, and lineation.
Field work is essential and integral part of geology. It involves mainly geological mapping. Field geology include methods, observation, and measurements; methods of location point, tape-and compass traverse methods; outcrop mapping; field work with sedimentary rocks, field work with igneous rocks, field work with metamorphic rocks; preparation of geological map, and writing geological report.
Surveying is the art of making measurement the distance, angles, elevations, direction, area and volume of natural and man-made features on the earth.
Environmental geology mainly concerns with the use and application of geoscientific knowledge and information lead to understanding of geologic hazards; proper use and care for earth resources; control and reduction of environmental pollution and degradation. This course includes geological hazards such as earthquake, landslide, volcanic eruptions; and hydrological hazards such as floods and coastal hazards.
This module concerns with the microscopic examination of minerals which should be mastered by all students of geology early in their careers. The aim of this module is to enable to identify minerals using petrographic microscope. This module covers principles of optical mineralogy, physical and optical properties of olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, mica, feldspar, feldspathoid, silica groups, and other important minerals such as garnet, tourmaline, carbonate, aluminosilicate group; gem minerals such as diamond, ruby, sapphire, emerald, aquamarine, peridot, jadeite.
This module focuses on Cleavage and Schistosity: origin, relation of cleavage and schistosity to major structures; Secondary Lineation: origin, types, relation of lineation to major structures; Structural Petrology or Petrofabrics; Continental Drift, Sea-floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics.
Field training course is design to provide a wide range of practical exercises and field experience in geology; observing, recording, mapping and problem solving. Assessment is to be made in the field by judging performance on field work, competency, etc. of students. Field duration is 15 days and the areas are Kyaukse Township, Mandalay Region, Sagaing Mountain and Sagaing Region.
This module emphasizes Human-induced Hazards and Problems; Using and Caring for Earth Resources; and Protection and Preservation of the Natural Environment in Myanmar.
This module deals with magma processes, field relations, texture, structures and classification of igneous rocks.
This module would be of beneficial to students getting knowledge of processes of sedimentation, properties of sediments, and the structure of sedimentary rocks.
This module emphasizes on all aspects of fossilized life found in the rocks and concern with Phylum- Protozoa, Phylum-Porifera, Phylum-Bryozoa, Phylum-Cniaria, Phylum-Protochora data.
This module deals Processes of Metamorphism, Agent of Metamorphism, Types of Metamorphism, Textures, and Classification of Metamorphic rocks.
This module concerns with Marine geology that is a branch of Oceanography dealing with phenomena ranging in scale from planetary to individual sediment particles.
This module consists of the data of igneous rocks such as petrography of various clans of the acid, intermediate, basic and ultramafic groups, pyroclastic rocks and lamprophyres; igneous associations at various plate boundries; igneous activity in Myanmar; and major Granitoid Belts of Myanmar.
This purpose of this module is to enable students to get the knowledge of clastic sedimentary rocks; chemical and organic sedimentary rocks; and depositional environments and facies.
This module deals with Systematic study of phyla Echinodermata; Arthropoda; Brachiopoda; and Mollusca; mentioning general features; morphological characteristics; classification; paleoecology; and stratigraphic importance. In addition, it introduces students to trace fossils.
Field training course is designed to provide a wide range of practical exercises and field experience in geology; observing, recording, mapping and problem solving. Assessment is made in the field by judging field conduct, competency, etc. of students. Duration of field training course is 21 days and areas included in Thazi Township, Kalaw Township and Mandalay Region.
This module consists of composition of the earth; thermodynamics, crystal and isotopes chemistry; the geochemical nature of the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere; the geochemical cycle and Introduction to exploration geochemistry.
It is mainly concerned with Geologic Time and Geochronology; Stratigraphic procedures; Stratigraphic Classification and Nomenclature; Sedimentary facies; Stratigraphic correlation; and Stratigraphic maps.
This module covered most of the geological information through the geological time emphasize on lower Paleozoic stratigraphy of Myanmar.
This purpose of this module is to enable students to familiarize data fundamental to understand the ore bearing fluid, ore forming processes and localization of ore deposits.
Photogeology is identification and interpretation of geological features by studying of a set of air-photo. It is design to provide the data of recognition of elements in air-photo interpretation; and air-photo interpretation characteristic of various rock types. In addition, students will enable to learn Remote Sensing.
This course contains two main parts; Engineering Geology and Hydrology. Engineering Geology is application of geological knowledge to the siting, design construction, operation and maintenance of civil engineering structure and facilities. Hydrogeology mainly concerns with origin and occurrence of groundwater, chemical characteristic of ground water.
This module covers most of the geological information about various minerals deposits of Myanmar.
This module covers most of the geological information through the geological time emphasize on Mesozoic and Tertiary stratigraphy of Myanmar.
This course emphasizes on exploration sequence, geophysical exploration methods, geochemical exploration methods for mineral exploration.
Field training course is designed to provide a wide range of practical exercises and field experience in geology; observing, recording, mapping and problem solving. In addition, these courses prepare students to enable writing geological field report and mapping projects. Each group has to submit report and mapping projects. Assessment is done during the field training by judging their interest, actively participation in field work, competency, etc. of students. Duration of field training is 21 days and the focus area is Ye Ngan Township in Southern Shan State.
This module concerns with the properties of gemstone and their identification; gem testing instruments; and enhancement of gemstone.
Optical mineralogy deals with the use of polarizing microscope under conoscopic arrangement. This module enables students to understand the optical properties of minerals, optic orientation diagrams, optic figures and their sign determination.
This module is designed by a combination of two topics: igneous petrology and metamorphic petrology; due to their similarity in approach and principles involved. It enables students a better understanding of modern classification of igneous rocks, phase mineralogy, petrographic model analysis, granitoid rocks of Myanmar, metamorphic facies and facies series, and plate tectonic and metamorphism.
This module enables students to understand modern remote sensing techniques, remote sensing application in mineral exploration and basic principles and procedure of geographic information system.
This module focuses on Plate Tectonic Theory; Plate tectonic and mineralization; Tectonics of South East Asia and geodynamic of India-Asia Collision.
It is a compulsory for every student to write a paper on assigned topics in one of the Study Fields: Mineralogy, Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Sedimentology, Paleontology, Structural geology, and Economic Geology. Seminar presentation and sitting examination on the paper submitted are compulsory.
This module is dealt with Regional Stratigraphy of South India and the Himalayas; Regional Stratigraphy of Thailand; Regional Stratigraphy of Yunan; Tertiary Stratigraphy of Assam and Indonesia.
This module presents two main parts: Vertebrate Paleontology and Micropaleontology. The purpose of Vertebrate Paleontology is to enable students to gain knowledge of Evolution of the Vertebrates, Fishes, Amphibian, Reptiles, Mamamals and Primate. Micropaleontology deals with a systematic study of some Foraminiferas.
This purpose of module is to enable students a better understanding of sedimentary environments, clastic rocks, carbonate rocks, clay minerals and mudstone.
Mining Geology is fundamental inductive knowledge of drilling, mining methods and mineral dressing.
This module is designed by a combination of Gemmology and Seismology. Gemmology concerns with advanced level of physical and optical properties of gem minerals, gem testing instruments, Identification of gems and grading.
It is a compulsory for every student to write a paper on assigned topics in one of the Study Fields: Mineralogy, Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology, Sedimentology, Paleontology, Structural geology, and Economic Geology. Seminar presentation and sitting examination on the paper that submitted are compulsory.
Field training course is designed to provide a wide range of practical exercises and field experience in geology; observing, recording, mapping and problem solving. In addition, these courses prepare students to enable writing geological field report and mapping projects. Each group has to submit report and mapping projects. Assessment is done during the field training by judging their interest, actively participation in field work, competency, etc. of students. . Duration of field training is 30 days and the focus area is Pyin Oo Lwin Township in Northern Shan State.
This module has two main courses: Photogeology and Remote Sensing. Photogeology course composed of morphology with spatial reference to air-photo interpretation; depositional landforms; and rock types and structure. Remote sensing deals with geologic mapping, in the development and evaluation of natural hazards.
This course covers all aspects of Micropaleontology, Ichnology and Conodonts which provides oil and gas exploration.
It is mainly concerned with the structural geology of the crust, although the processes and structures described are relevant also for deformation that occurs at deeper levels within our planet. This course focuses on Stress and Strain in two dimensions; Behavior of rock deformation; Dynamic of faulting; Analysis of micro structures; Petrofabric; and Morphotectonics
This course presents the geochemical characteristics of magmas in relationship to their tectonic setting. Igneous Petrology course focuses on the basic foundation in petrological principles, including elementary geochemistry phase diagrams, mineralogy, regional geology and global tectonics. Metamorphic Petrology course emphasizes on metamorphic facies and facies series; metamorphic epoch; metamorphic belts of Myanmar; and geochemical cycle.
Environmental Geology is mainly focuses on the fascinating interaction between humans and the geologic processes. This course explains how human survival is highly dependent on the natural environment. Environmental geology is geology applied to living. Students will examine how geologic processes and hazards influence human activities; the geologic aspects of pollution; and waste-disposal problems.
This module enables students to understand recent advances in plate tectonic, magmatism, metamorphism, sedimentation, and metallogeny along different plate boundaries, and Geodynamics of Southeast Asia.
This module deals with Clay minerals; Mud rocks; Turbidites; Flysch and Molasses; and Sedimentation as ore genesis. Applied sedimentary provides a firm foundation on which interpret sediment remotely sensed.
This purpose of this module is enable students to gain knowledge about stratigraphic invertebrate paleontology of Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic rock sequences.
This course deals with analytical methods pertaining to mineralogy and petrochemisty geologic mapping statistical methods.
The purpose of this module is to enable students to familiarize with recent advances in geological sciences that relevant to students’ research fields.
This module deals with literature survey, how to review the literature, how to write a thesis, and how to make presentation that correspond to students’ field of research.
Sedimentologic concept uses depositional anatomy to reconstruct environments and lateral facies changes about alluvia, deltic, estuarne lastic shore line carbonate platform, abyssal and trench. It is part of stratigraphy as it studies the vertical succession of sedimentary rocks and their succession and correlation.