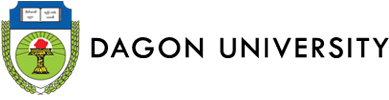Dr. Khin Hnin Aye
ဒေါက်တာဒေါ်ခင်နှင်းအေး
Position : Professor (Head)
Degree : B.Sc (Hons), M.Sc, Ph.D (Industrial Chemistry)
Industrial Chemistry
Position : Professor
Degree : B.Sc (Hons), M.Sc,M. Res Ph.D (Industrial Chemistry)
Teacher list
| Sr.No | Department | Name | Position | Education | Thesis Title | Field Of Specialization | Current Research Project | Email/Gmail |
| 1 | Industrial Chemistry | Dr. Khin Hnin Aye | Professor (Head) | Ph.D | Dehydration of Selected Vegetables by Different Drying Methods | Food | – | [email protected] |
| 2 | Industrial Chemistry | Dr. Khin Mar Hlaing | Professor | Ph.D | Preparation of Bagasse-based Composite Materials | Environmental Science | – | [email protected] |
| 3 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Shwe Sin Win | Associate Professor | M.Sc | – | – | – | [email protected] |
| 4 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Latt Latt Lwin | Lecturer | M.Sc | An Investigation into the Reduction of Toxicity in Some Bamboo Shoots Products | Food | – | [email protected] |
| 5 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Nang Phyoe Phyoe Oo | Lecturer | M.Sc | Study on Preparation of Toddy Palm Syrup (Group Project) | Food | – | [email protected] |
| 6 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Mya Thandar | Lecturer | M.Sc | – | – | – | [email protected] |
| 7 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Myat Thin Yanant Aung | Demonstrator | M.Sc | Preparation and Characterization of Fish (Ngar-Shwe) Seasoning Powder for Myanmar Traditional Food | Food | – | [email protected] |
| 8 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Lai Win Phyu | Demonstrator | M.Sc | Study on the Taste and Flavor of Processed Rohu | Food | – | [email protected] |
| 9 | Industrial Chemistry | Daw Hnin Si | Demonstrator | M.Sc | Preparation of Organic Liquid Fertilizer from Fish Waste | Food Waste Utilization | – | [email protected] |
Programmes Offered
- B.Sc. / B.Sc. (Hons) in Industrial Chemistry
- M.Sc. and M.Res. in Industrial Chemistry
Curriculum
B.Sc. in Industrial Chemistry
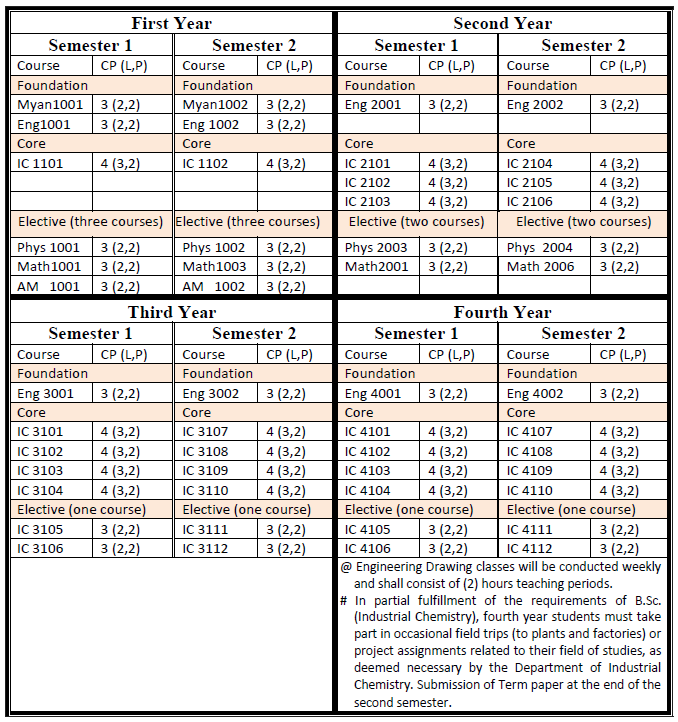
B.Sc. (Honours) in Industrial Chemistry
Students who passed second year with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend B.Sc. Honours classes for three more years. After finished successfully, they are earned B.Sc. (Hons) degree majoring in Industrial Chemistry.
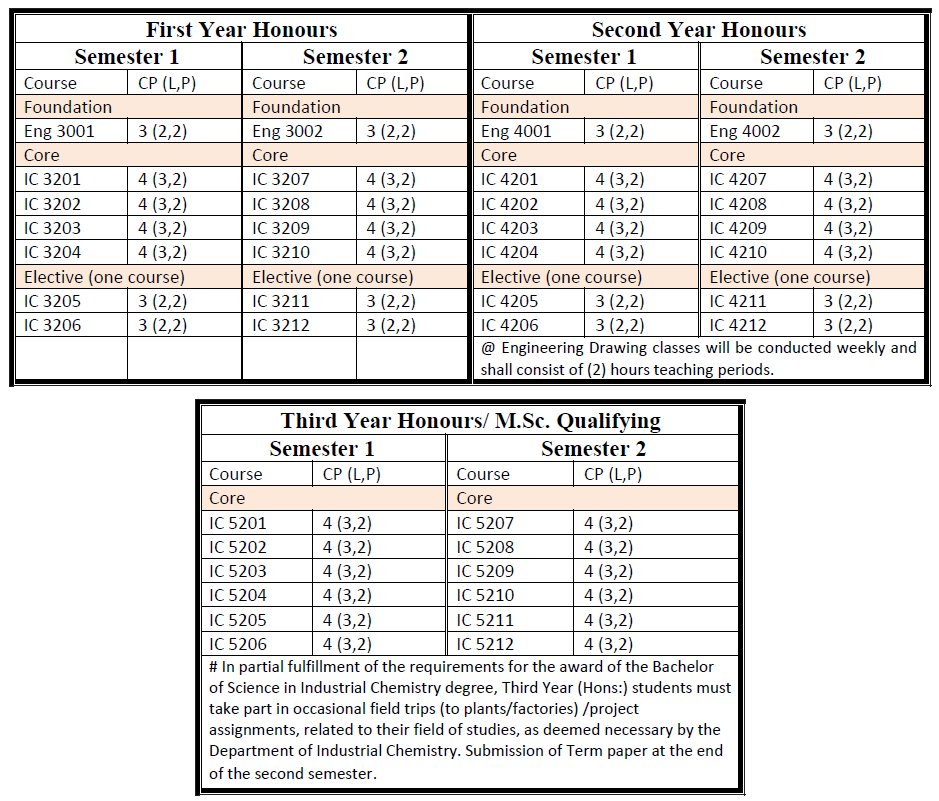
M.Sc. in Industrial Chemistry
Students who passed B.Sc. (Hons) with GPA greater than 4 are eligible to attend M.Sc. classes for two more years. After finished successfully, they are earned M.Sc. degree majoring in Industrial Chemistry.
Fields of research currently conducting at the department are fundamental and applied researches in organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, food science, cosmetic technology and environment science.
Course Descriptions
This module covers a broad sense on Hydrolysis, Esterification and Oxidation. Hydrolysis: Definition and Scope, Hydrolyzing Agents, Materials Susceptible to Hydrolysis, Equipment for Hydrolysis, and Technical Operations Involving Hydrolysis; Esterification: Esterification by Organic Acids, Esterification of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives, Esters by Addition to Unsaturated Systems, Esters of Inorganic Acids, and Esterification Practice; Oxidation: Types of Oxidative Reactions, Oxidizing Agents, Liquid Phase Oxidation with Oxidizing Compounds, Vapour Phase Oxidation of Aliphatic Compounds, Vapour Phase Oxidation of Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Apparatus for Oxidation.
This module covers 1) Nitration: Introduction, Nitrating Agents, Aromatic Nitration, Kinetics and Mechanism of Aromatic Nitration, Nitration of Paraffinic Hydrocarbons, Nitrate Esters, N-Nitro Compounds, Thermodynamics of Nitrations, Process Equipment for Technical Nitration, Mixed Acid for Nitrations, Typical Industrial Nitration Processes and 2) Sulfonation and Sulfation.
The module is designed to learn about Chemical Reaction Engineering; Reactor Design- Introduction to Reactor Design, Single Ideal Reactors; Heat Effects; and Flow Behaviour of Reactor.
In the first semester, students will learn IC 5206 that includes the Characteristics of Bio-Products and Lipid Biosynthesis. In the second semester, students will learn IC 5212 that covers Food and Enzymes Produced by Microorganisms and Fermentation and Other uses of Microorganisms.